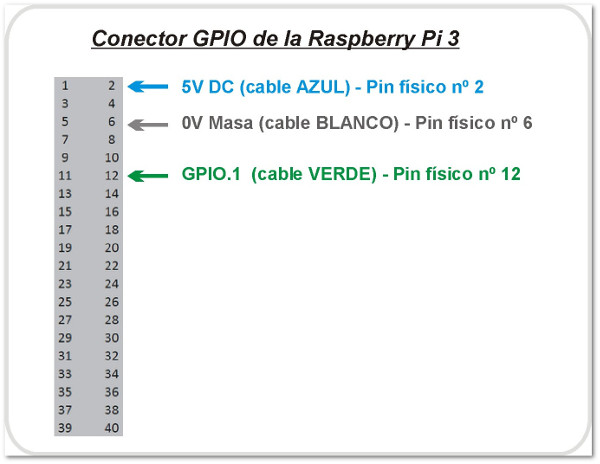
Relé controlado por la Raspberry Pi 3 con programación en Java.
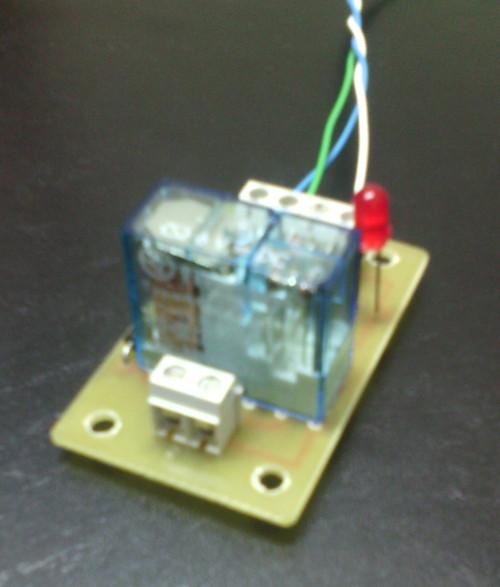
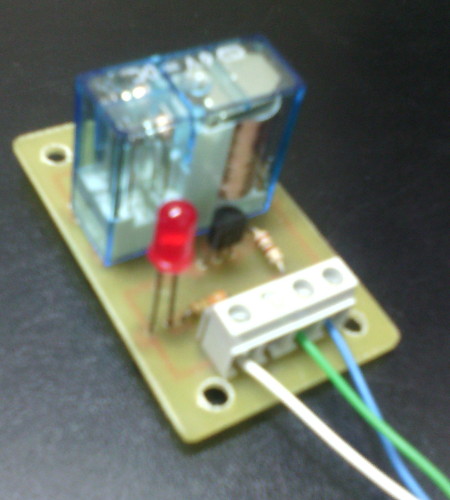
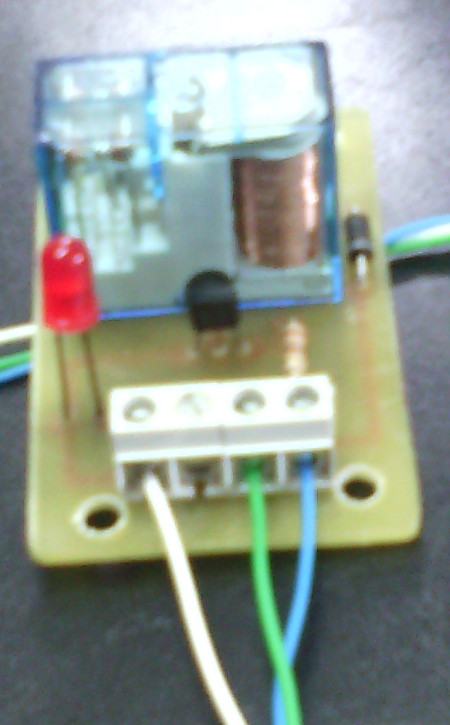
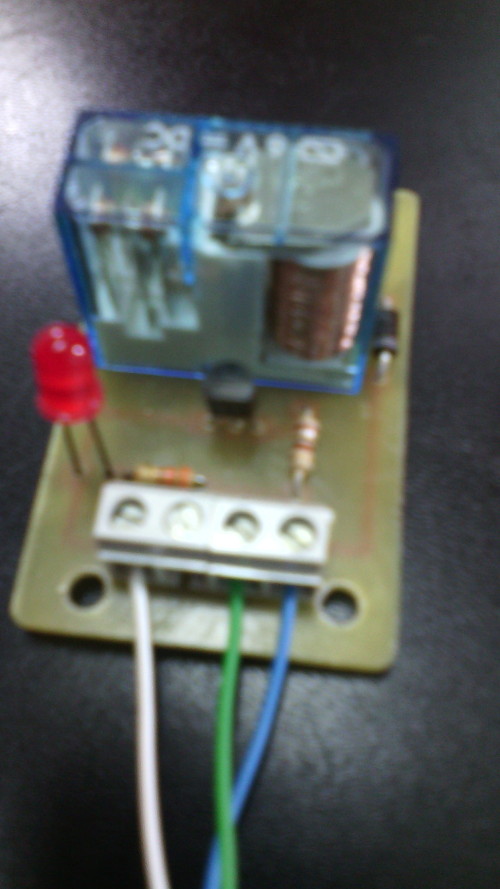
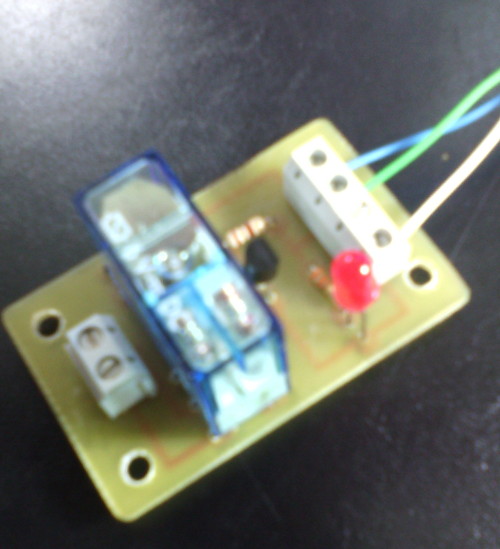
La Raspberry Pi remite la señal de activación por el pin GPIO.1 (pín físico 12, cable VERDE). Esa señal se envía a través de una resistencia de 100 Ohmios a la base del transistor NPN (C945). En el colector del transistor se ha conectado el pin físico 2 de la Raspberry Pi 3 que facilita 5V DC (cable azul). Al recibir señal por el GPIO.1, el transitor conmuta y hace llegar los 5V a la bobina del relé. También se ha acoplado a la llegada de la señal GPIO.1 un led con su correspondiente resistencia limitadora (330 Ohms) de forma que al recibir la señal de activación de la Raspberry, se activa el relé y el led. La masa (0V) está conectada al pin físico 6 (cable BLANCO).
El programa Java lo he obtenido de "The Pi4J Project - Java I/O library for the Raspberry Pi": http://pi4j.com/
Es necesario instalar las clases que utiliza este projecto según se indica en la página: http://pi4j.com/install.html
Orden para compilar el programa...
javac -classpath .:classes:/opt/pi4j/lib/'*' ControlGpioExample.java
Orden para ejecutar el programa...
java -classpath .:classes:/opt/pi4j/lib/'*' ControlGpioExample
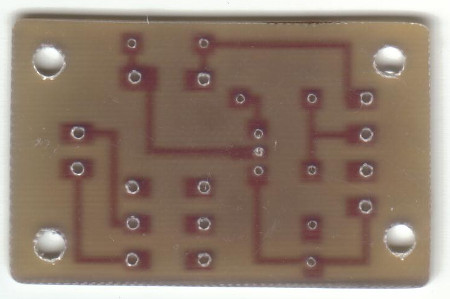
Componentes y placa de circuito...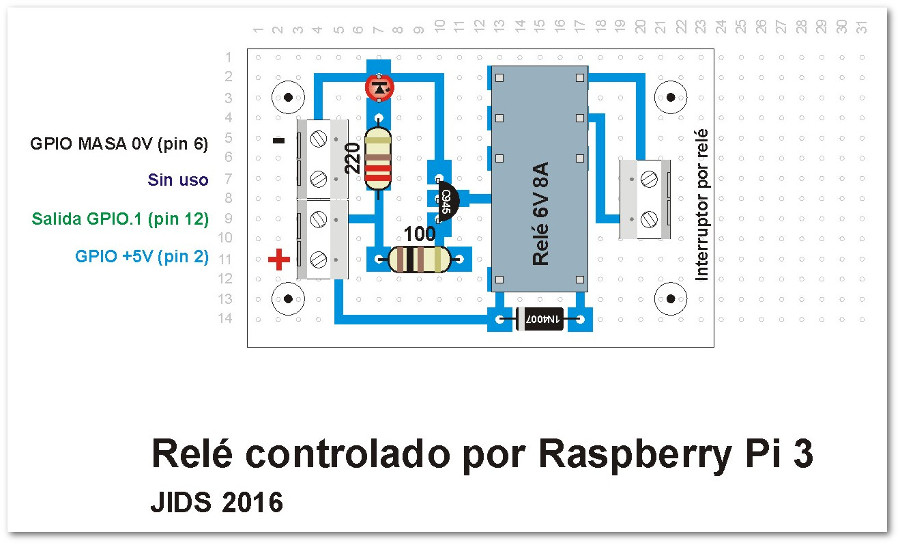
Pistas (tamaño del circuito impreso: 57mm x 36mm)
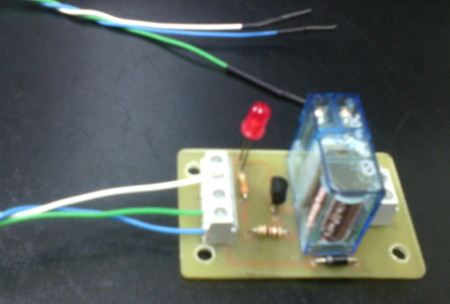
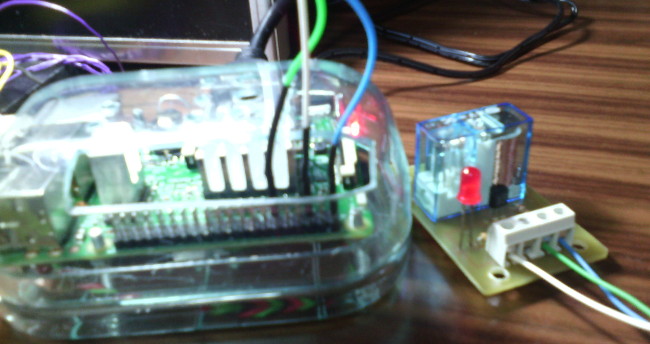
Imágenes del montaje
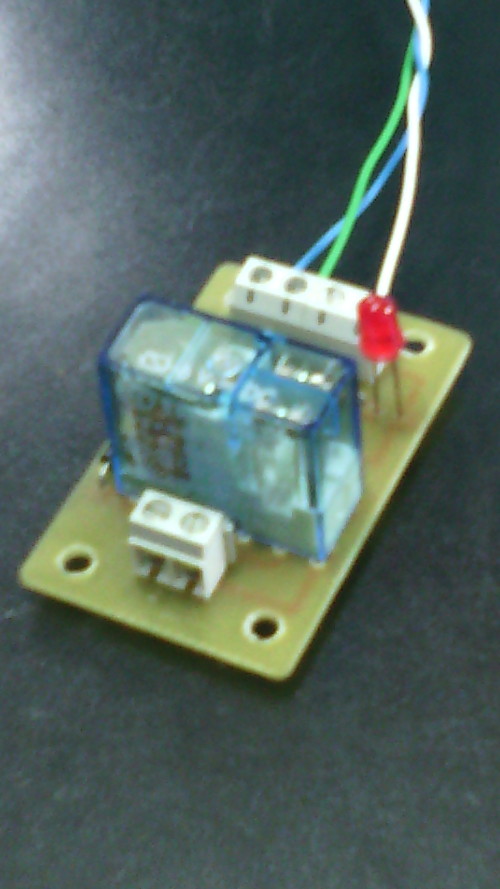
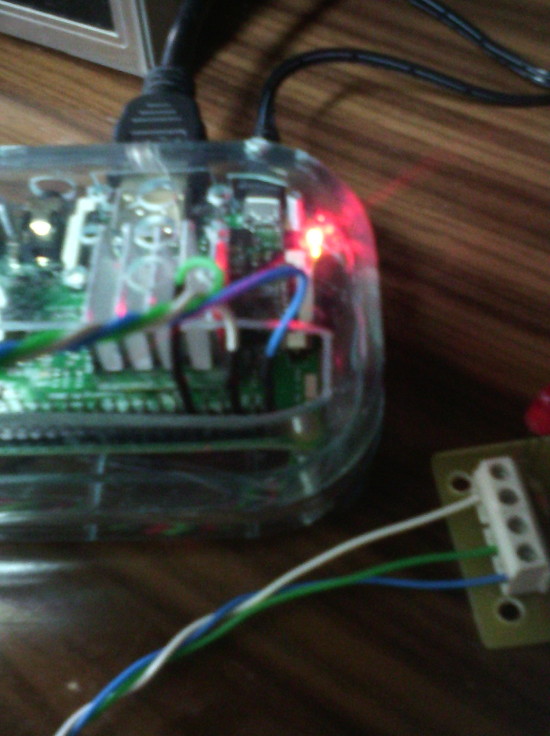
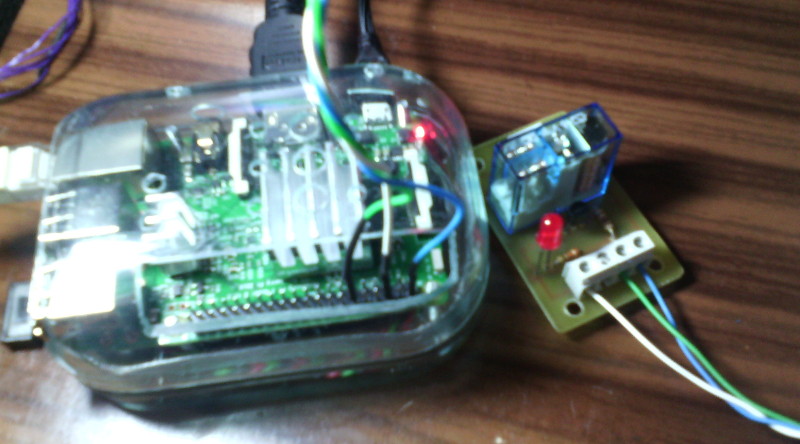



Programa en Java que activa y desactiva varias veces el relé con diferentes tiempos de activación para hacer pruebas del funcionamiento.
// START SNIPPET: control-gpio-snippet
/*
* #%L
* **********************************************************************
* ORGANIZATION : Pi4J
* PROJECT : Pi4J :: Java Examples
* FILENAME : ControlGpioExample.java
*
* This file is part of the Pi4J project. More information about
* this project can be found here: http://www.pi4j.com/
* **********************************************************************
* %%
* Copyright (C) 2012 - 2016 Pi4J
* %%
* This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
* published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the
* License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Lesser Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Lesser Public
* License along with this program. If not, see
* <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-3.0.html>.
* #L%
*/
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioController;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioFactory;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.GpioPinDigitalOutput;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.PinState;
import com.pi4j.io.gpio.RaspiPin;
/**
* This example code demonstrates how to perform simple state
* control of a GPIO pin on the Raspberry Pi.
*
* @author Robert Savage
*/
public class ControlGpioExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("<--Pi4J--> GPIO Control Example ... started.");
// create gpio controller
final GpioController gpio = GpioFactory.getInstance();
// provision gpio pin #01 as an output pin and turn on
final GpioPinDigitalOutput pin = gpio.provisionDigitalOutputPin(RaspiPin.GPIO_01, "MyLED", PinState.HIGH);
// set shutdown state for this pin
pin.setShutdownOptions(true, PinState.LOW);
System.out.println("--> GPIO state should be: ON");
Thread.sleep(500);
// turn off gpio pin #01
pin.low();
System.out.println("--> GPIO state should be: OFF");
Thread.sleep(300);
// toggle the current state of gpio pin #01 (should turn on)
pin.toggle();
System.out.println("--> GPIO state should be: ON");
Thread.sleep(500);
// toggle the current state of gpio pin #01 (should turn off)
pin.toggle();
System.out.println("--> GPIO state should be: OFF");
Thread.sleep(100);
// turn on gpio pin #01 for 1 second and then off
System.out.println("--> GPIO state should be: ON for only 1 second");
pin.pulse(1000, true); // set second argument to 'true' use a blocking call
// stop all GPIO activity/threads by shutting down the GPIO controller
// (this method will forcefully shutdown all GPIO monitoring threads and scheduled tasks)
gpio.shutdown();
System.out.println("Exiting ControlGpioExample");
}
}
//END SNIPPET: control-gpio-snippet
Descargar código fuente: "ControlGpioExample.java"